Why is Carbon Pricing Crucial for ESG’s Climate Action?
ACRYPT Consulting
Carbon pricing is a powerful approach aimed at reducing carbon emissions, aka GHG emissions. It plays a crucial role in #ESG initiatives. It operates through market mechanisms that hold emitters accountable for the costs associated with releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
At its core, carbon pricing upholds the principle of “polluter pays,” ensuring that those responsible for emissions bear the economic consequences of their actions. This mechanism establishes a financial incentive to drive a shift away from high-emission practices towards sustainable alternatives.
𝙎𝙞𝙜𝙣𝙞𝙛𝙞𝙘𝙖𝙣𝙘𝙚 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙞𝙢𝙥𝙖𝙘𝙩 𝙤𝙣 𝙀𝙎𝙂 𝙤𝙗𝙟𝙚𝙘𝙩𝙞𝙫𝙚𝙨:
🌲 Environmental Impact: Carbon pricing curbs emissions, addressing climate change at its core. It drives renewable energy adoption, and reforestation, promoting environmental stewardship within ESG frameworks.
💰 Economic Implications: The “polluter pays” principle redirects investments to low-carbon technologies, fostering a green economy and, aligning with the “E” in ESG.
👨🌾 Social Responsibility: Beyond the environment, carbon pricing spurs social initiatives, benefiting communities and, enhancing social responsibility within ESG strategies.
🌊 Climate Risk Management: Carbon pricing signals climate costs, driving proactive risk management, and long-term resilience in a carbon-constrained world.
💡 Technological Innovation: By incentivizing emission reduction, carbon pricing encourages clean technology investment, accelerating the transition to a low-carbon future.
💹 Green Finance and ESG Investing: Carbon pricing fuels #sustainablefinance & ESG-conscious investments, channeling capital to climate-aligned solutions.
🤝 Global Climate Commitments: Carbon pricing aligns with international climate agreements, demonstrating commitment to climate action and global sustainability.
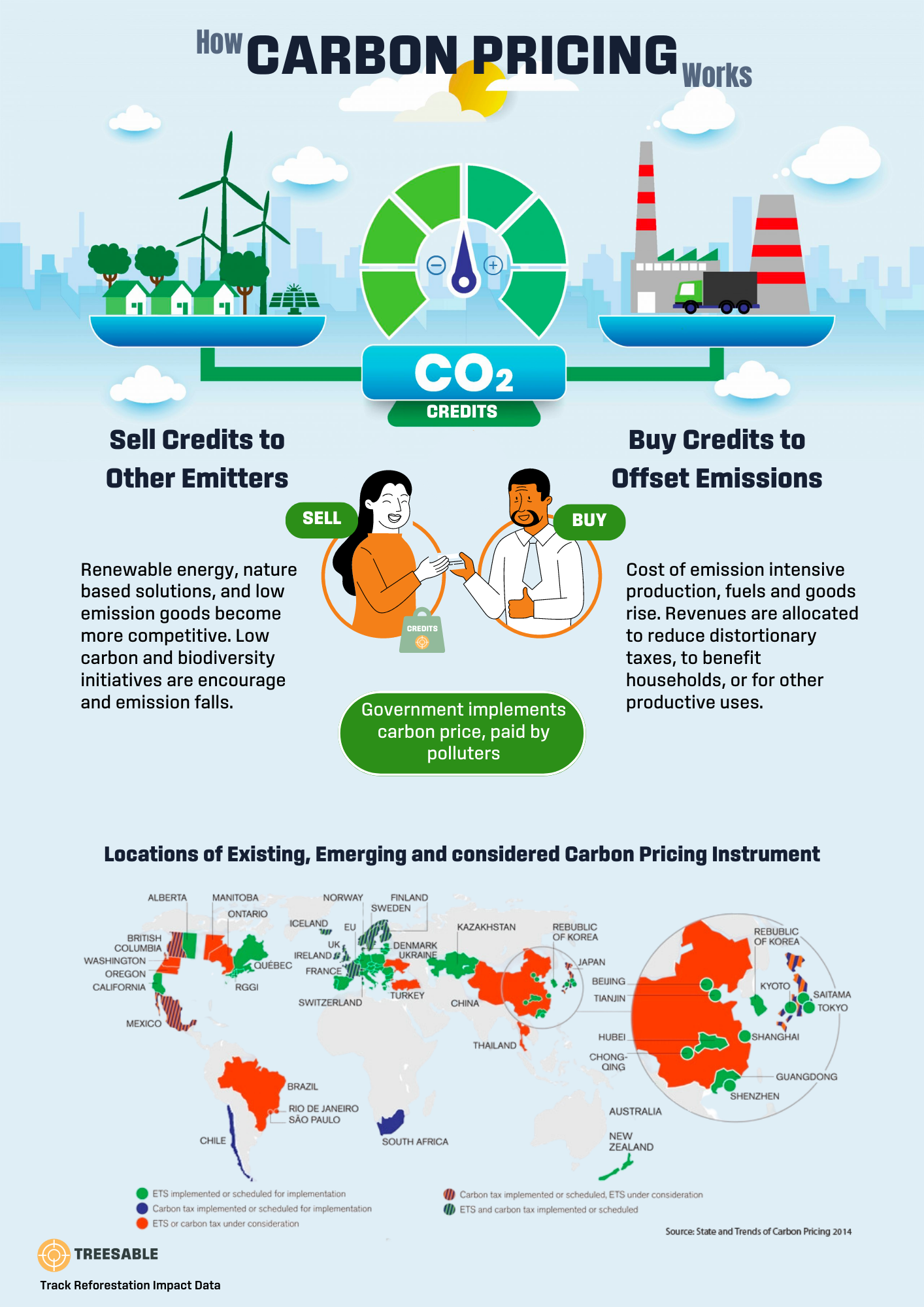
𝗛𝗼𝘄 𝗱𝗼 𝗩𝗮𝗿𝗶𝗼𝘂𝘀 𝗖𝗮𝗿𝗯𝗼𝗻 𝗣𝗿𝗶𝗰𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗜𝗻𝘀𝘁𝗿𝘂𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀 𝗪𝗼𝗿𝗸?
🔸 Carbon Tax: Directly assigns a price to GHG emissions, incentivizing entities to lower emissions through efficient processes and cleaner energy sources.
🔸 Emission Trading System (ETS): Sets a “cap” on GHG emissions, allowing trading of carbon permits to promote cost-effective emission reductions.
🔸 Crediting Mechanism: Assigns credits to emissions reductions from projects or policies, enabling entities to offset emissions by buying verified credits.
🔸 Results-Based Climate Finance (RBCF): Provides funds to entities achieving climate-related goals like emissions reductions.
🔸 Internal Carbon Pricing: Governments and companies implement internal pricing, influencing investment decisions with a hypothetical cost or internal carbon fee.
If you’re eager to learn how to implement ESG reporting into your business, I’m here to help. Let’s collaborate on achieving your science-based targets and fostering community-driven stewardship.
Let’s connect on Linkedin! 🌳🤝
Carbon pricing signals climate costs, driving proactive risk management, and long-term resilience in a carbon-constrained world.
Carbon pricing aligns with international climate agreements, demonstrating commitment to climate action and global sustainability.
Beyond the environment, carbon pricing spurs social initiatives, benefiting communities and, enhancing social responsibility within ESG strategies.
Ready to Grow?
Get in Touch
Contact
Copenhagen, Denmark 2100
Email us


