What is Double Materiality and its Role in ESG Reporting?
ACRYPT Consulting
Materiality in ESG refers to the identification and evaluation of #sustainability issues that affect organizations. It enables companies to prioritize impactful issues for effective decision-making. The emergence of double materiality has further enhanced the role of materiality in #ESGreporting.
ESG materiality encompasses two dimensions: impact materiality and financial materiality.
Impact Materiality examines an organization’s impact on the environment, society, and economy. It focuses on understanding the external effects of a company’s operations. Financial Materiality considers how environmental factors influence an organization financially. It highlights the risks and opportunities companies face, aligning sustainability with financial performance.
Reporting standards like #sasb and #gri have distinct interpretations of materiality, influencing their approach. SASB adopts an inward financial definition, identifying sustainability issues likely to affect an organization’s financial performance. GRI takes an outward definition, considering information important for reflecting an organization’s social and environmental impacts.
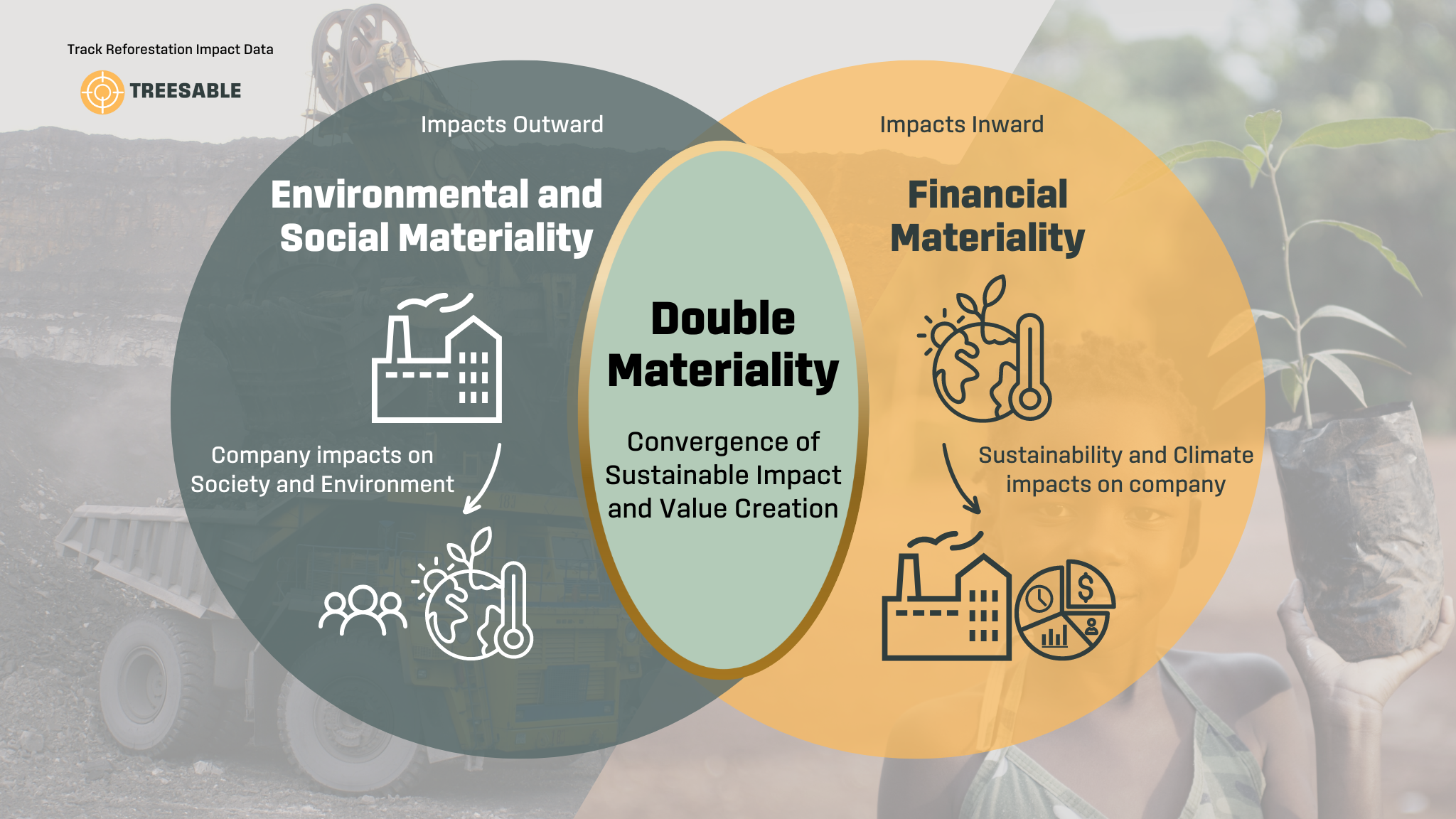
#Climatechange exemplifies double materiality, requiring organizations to consider both inward and outward impacts.
➡ Inward Impact: Companies assess physical and financial risks associated with climate change, including severe weather’s effects on assets, production, and supply chains.
⬅ Outward Impact: Organizations measure their greenhouse gas emissions to evaluate environmental impacts, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Materiality should be an ongoing process, continuously assessing issues to adapt to changing circumstances. Prioritizing material issues based on their actual impact rather than convenience is vital for effective sustainability management.
Effective double materiality assessments:
🌳 Utilize Industry Standards and Tools: Industry standards like the CSB Materiality Map, SDGs, and TCFD guidelines provide a foundation for identifying materiality specific to their industry.
🌳 Manage Stakeholders Effectively: Engaging stakeholders as valuable sources of information helps identify blind spots and areas for enhanced sustainability efforts.
🌳 Incorporate Materiality into Business Strategy: Embed materiality as a core element in the overall business strategy, integrating ESG risks and opportunities into risk management processes for generating business value and facilitating internal change.
Understanding double materiality is crucial for companies committed to sustainability and effective ESG risk and opportunity management.
If you’re eager to learn how to implement ESG reporting into your business, I’m here to help. Let’s collaborate on achieving your science-based targets and fostering community-driven stewardship.
Let’s connect on Linkedin! 🌳🤝
Industry standards like the CSB Materiality Map, SDGs, and TCFD guidelines provide a foundation for identifying materiality specific to their industry.
Engaging stakeholders as valuable sources of information helps identify blind spots and areas for enhanced sustainability efforts.
Embed materiality as a core element in the overall business strategy, integrating ESG risks and opportunities into risk management processes for generating business value and facilitating internal change.
Ready to Grow?
Get in Touch
Contact
Copenhagen, Denmark 2100
Email us


